在上一章我们分析了SpingBoot启动流程中实例化SpingApplication的过程。
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
这篇文章咱么说下run()方法开始之后都做了那些事情。
继续往下跟着源码进入到run()这个是比较核心的一个方法了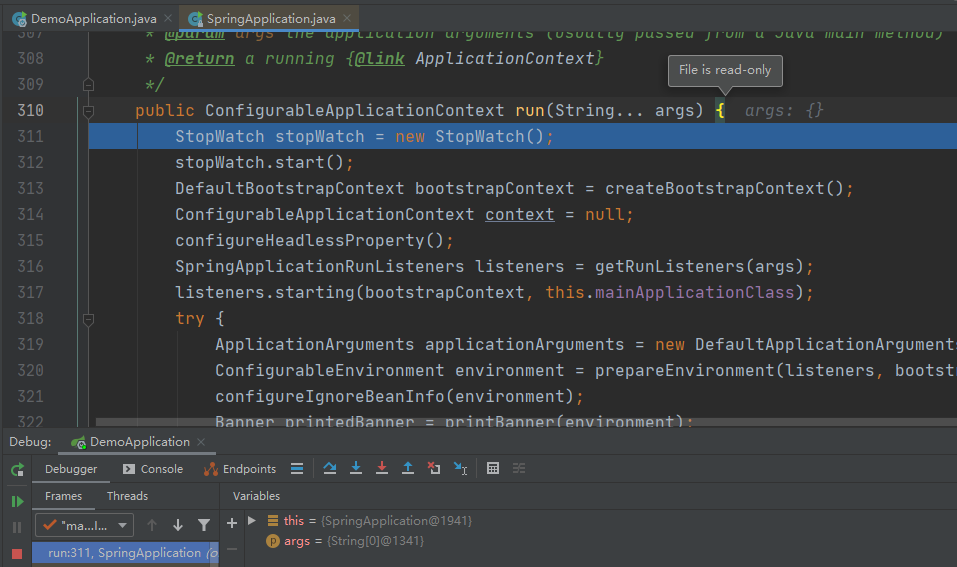
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); // 计时器开始 stopWatch.start(); // 创建启动上下文对象 DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; // 配置Handless模式,是在缺少显示屏、键盘或鼠标时的系统配置 // 默认为true configureHeadlessProperty(); //获取并启动监听器 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); // 启动监听器 listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass); try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); // 准备环境 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments); // 忽略配置的bean configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); // 打印banner,就是启动的时候在控制台的spring图案 Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); // 创建容器 context = createApplicationContext(); context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup); // 准备应用上下文(spring容器前置处理) prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); // 刷新容器 refreshContext(context); // 刷新容器后的扩展接口(spring容器后置处理) afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); // 结束计时器并打印,这就是我们启动后console的显示的时间 stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } // 发布监听应用上下文启动完成(发出启动结束事件) listeners.started(context); // 执行runner callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable ex) { // 异常处理,如果run过程发生异常 handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } try { // 监听应用上下文运行中 listeners.running(context); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, null); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } // 返回最终构建的容器对象 return context; }接下来就对上面的关键步骤一一解释
1. 获取所有的监听器
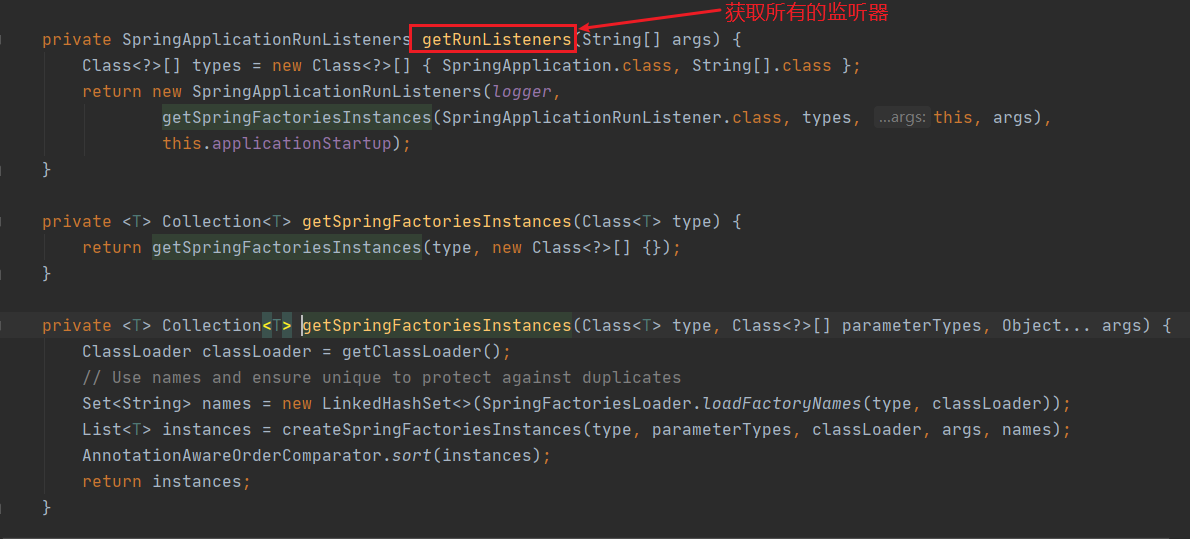
这段代码我们比较熟悉了,上一篇咱么详细介绍过,它的主要作用就是去META-INFO/spring.factories 中加载配置SpringApplicationRunListener的监听器如下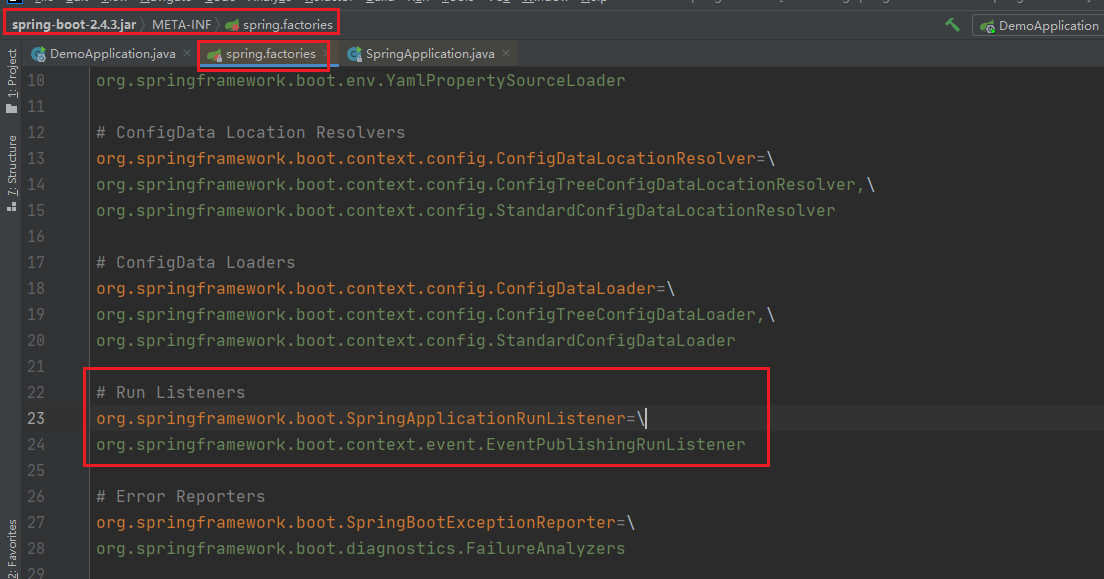
显然只有一个事件发布监听器类,拿到了EventPublishingRunListener启动事件发布监听器,下一步就是开始启动了listeners.starting();我们往下跟源码看
@Override public void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) { this.initialMulticaster .multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(bootstrapContext, this.application, this.args)); }启动的时候实际上是又创建了一个ApplicationStartingEvent对象,其实就是监听应用启动事件。
其中 initialMulticaster是一个SimpleApplicationEventMuticaster
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) { ResolvableType type = eventType != null ? eventType : this.resolveDefaultEventType(event); // 获取线程池,为每个监听事件创建一个线程 Executor executor = this.getTaskExecutor(); // 根据ApplicationStartingEvent事件类型找到对应的监听器,并迭代 Iterator var5 = this.getApplicationListeners(event, type).iterator(); while(var5.hasNext()) { ApplicationListener<?> listener = (ApplicationListener)var5.next(); if (executor != null) { // executor.execute(() -> { this.invokeListener(listener, event); }); } else { this.invokeListener(listener, event); } } }2.准备环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) { // Create and configure the environment // 这里我们加入了web依赖所以是一个servlet容器 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment(); // 配置环境 configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs()); // 环境准备完成 ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment); listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment); DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment); configureAdditionalProfiles(environment); bindToSpringApplication(environment); if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) { environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass()); } ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment); return environment; }由于我们是添加了web的依赖 getOrCreateEnvironment()返回的是一个standardservletEnviroment 标准的servlet环境
2.1 配置环境
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) { if (this.addConversionService) { // 嵌入式的转换器 ConversionService conversionService = ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance(); environment.setConversionService((ConfigurableConversionService) conversionService); } // 配置属性资源文件 configurePropertySources(environment, args); // 配置文件 configureProfiles(environment, args); }应用嵌入的转换器ApplicationConversionService
public static void configure(FormatterRegistry registry) { DefaultConversionService.addDefaultConverters(registry); DefaultFormattingConversionService.addDefaultFormatters(registry); // 格式转换 addApplicationFormatters(registry); // 类型转换 addApplicationConverters(registry); } ===============格式转换================= public static void addApplicationFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) { registry.addFormatter(new CharArrayFormatter()); registry.addFormatter(new InetAddressFormatter()); registry.addFormatter(new IsoOffsetFormatter()); } ========================类型转换=================== public static void addApplicationConverters(ConverterRegistry registry) { addDelimitedStringConverters(registry); registry.addConverter(new StringToDurationConverter()); registry.addConverter(new DurationToStringConverter()); registry.addConverter(new NumberToDurationConverter()); registry.addConverter(new DurationToNumberConverter()); registry.addConverter(new StringToPeriodConverter()); registry.addConverter(new PeriodToStringConverter()); registry.addConverter(new NumberToPeriodConverter()); registry.addConverter(new StringToDataSizeConverter()); registry.addConverter(new NumberToDataSizeConverter()); registry.addConverter(new StringToFileConverter()); registry.addConverter(new InputStreamSourceToByteArrayConverter()); registry.addConverterFactory(new LenientStringToEnumConverterFactory()); registry.addConverterFactory(new LenientBooleanToEnumConverterFactory()); if (registry instanceof ConversionService) { addApplicationConverters(registry, (ConversionService) registry); } } 2.2 环境准备完成
同上面启动监听事件,这次的环境准备也是同样的代码
@Override public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent( // 创建一个应用环境准备事件对象 new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(bootstrapContext, this.application, this.args, environment)); }debug进去之后代码跟AppLicationstrigevent 事件对象是一样的。不再赘述。
不过这里是7个监听器对象
3.配置忽略的bean
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
4.打印banner
这是SpringBoot默认的启动时的图标
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
这个是可以自定义的,也可以是图篇或是文本文件中的图形
5.创建容器
紧接着上一篇,接下来就是创建容器
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() { return this.applicationContextFactory.create(this.webApplicationType); }6.准备应用上下文
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) { // 设置环境参数 context.setEnvironment(environment); // 设置后处理应用上下文 postProcessApplicationContext(context); //把从spring.factories中加载的org.springframework.bt.context.ConfigurationwarningsApplicationContextIitiaLizer,进行初始化操作 applyInitializers(context); //EventPubLishingRunListener发布应用上下文事件 listeners.contextPrepared(context); // 打印启动日志 bootstrapContext.close(context); if (this.logStartupInfo) { logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null); logStartupProfileInfo(context); } // Add boot specific singleton beans ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments); if (printedBanner != null) { //注册一个字是springAppLicationArguments单例的bean beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner); } if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) { ((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory) .setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding); } if (this.lazyInitialization) { context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor()); } // Load the sources 获取所有资源 Set<Object> sources = getAllSources(); Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty"); // 创建BeanDefinitionLoader加载器加载注册所有的资源 load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0])); // 同之前,发布应用上下文 加载事件 listeners.contextLoaded(context); }7.刷新应用上下文
刷新应用上下文就进入了spring的源码了
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) { StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh"); // Prepare this context for refreshing. //准备刷新上下文 this.prepareRefresh(); // Tetl the subclass to refresh the internal bean facto // 通知子类刷新内部工厂 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. // 准备Bean工厂 this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in contex t subc lasses. // 允许在上下文子类中对bean工厂进行后处理。 // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context, this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process"); this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // 注册后置处理器。 this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); beanPostProcess.end(); // 初始化信息源 this.initMessageSource(); // 初始化上下文事件发布器 this.initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // 初始化其他自定义bean this.onRefresh(); // 注册监听器 this.registerListeners(); this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); //完成刷新,清缓存,初始化生命周期,事件发布等 this.finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException var10) { if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) { this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var10); } // 销毁bean this.destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active'flag. this.cancelRefresh(var10); throw var10; } finally { this.resetCommonCaches(); contextRefresh.end(); } } }刷新的代码有点深,也是在这时创建了Tomcat对象,这也是SpringBoot** 一键启动**web工程的关键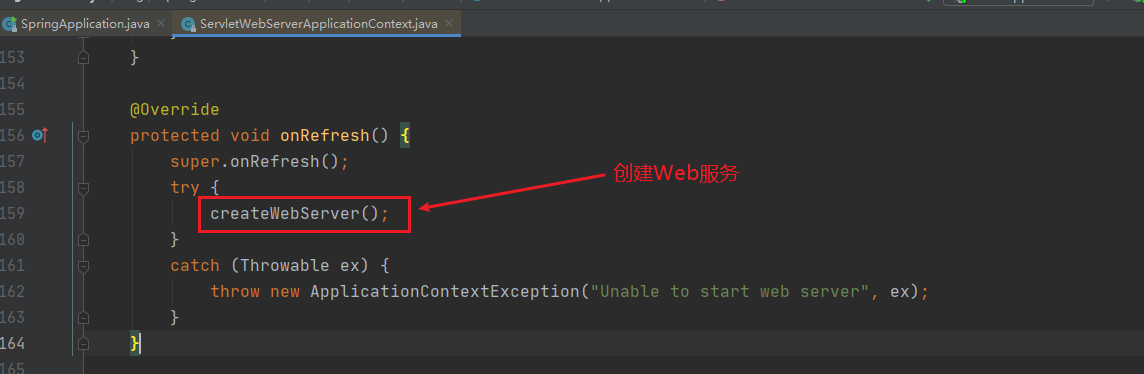
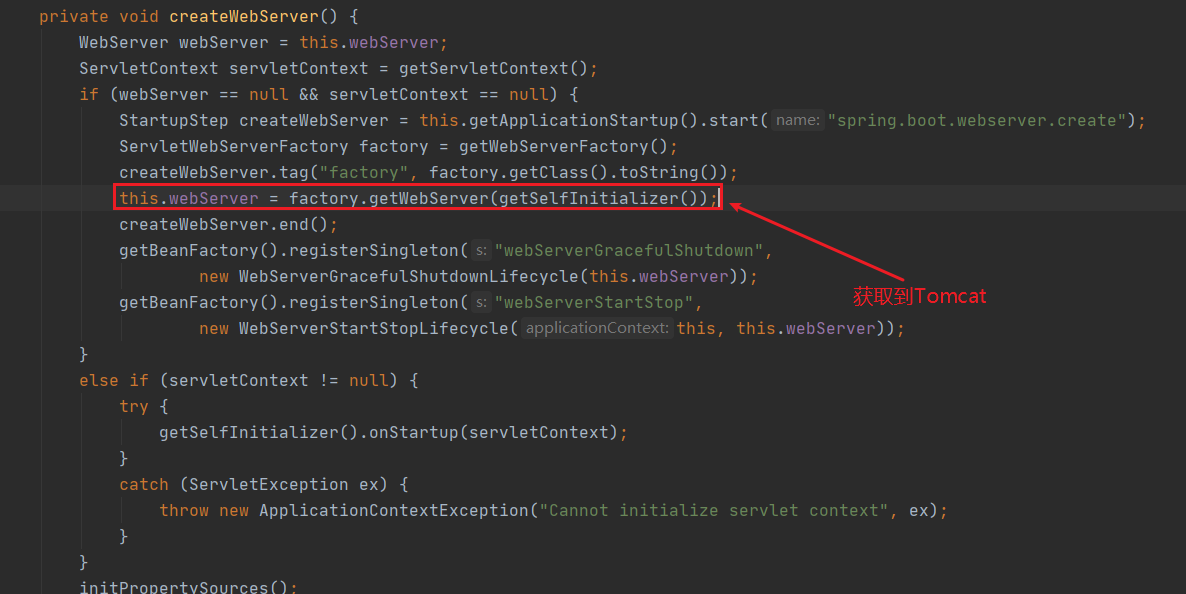
创建了Tomcat对象,并设置参数
@Override public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) { if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) { Registry.disableRegistry(); } Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat(); File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat"); tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath()); Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol); connector.setThrowOnFailure(true); tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector); customizeConnector(connector); tomcat.setConnector(connector); tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false); configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine()); for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) { tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector); } prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers); // 返回TomcatWebServer服务 return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat); }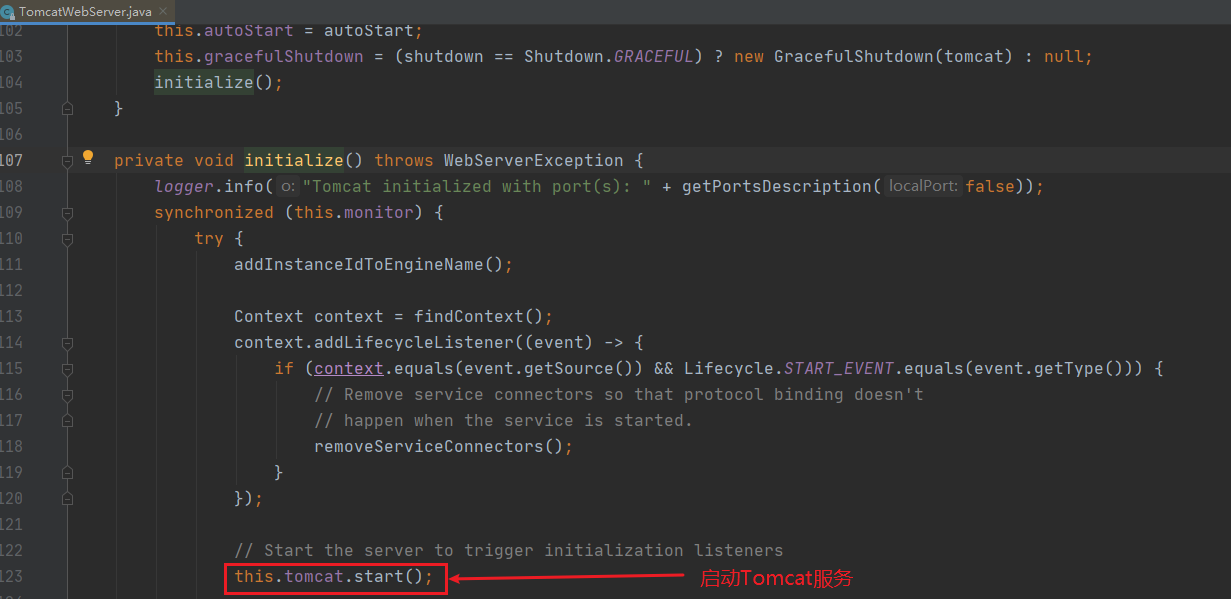
8.刷新后处理
afterReftesh();//是个一空实现,留着后期扩展
/** * Called after the context has been refreshed. * @param context the application context * @param args the application arguments */ protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) { }9.发布监听应用启动事件
@Override public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { context.publishEvent(new ApplicationStartedEvent(this.application, this.args, context)); AvailabilityChangeEvent.publish(context, LivenessState.CORRECT); }这里是调用context.publishEvent()方法,发布应用启动事件ApplicationStartedEvent.
10.执行Runner
获取所有的ApplicationRuner和CommandLineRunner来初始化一些参数,callRuner(是一个回调函数)
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) { List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>(); runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values()); runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values()); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners); for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) { if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) { callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args); } if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) { callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args); } } }11.发布上下文准备完成的事件
listeners.running(context);
@Override public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { context.publishEvent(new ApplicationReadyEvent(this.application, this.args, context)); AvailabilityChangeEvent.publish(context, ReadinessState.ACCEPTING_TRAFFIC); }这段代码看上去似成相识,前面有很多类似的代码,不同的是这里上下文准备完成之后发布了一个ApplicationReadyEvent事件,声明一下应用上下文准备完成。
小结
这篇主要是介绍了SpringBoot启动过程中run()的这个过程。从中我们也可以发现一些非常好的编码习惯,大家可以在日常的工作中从模仿到内化,慢慢变成自己的东西。
原文转载:http://www.shaoqun.com/a/610572.html
洋老板:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/2779
csa:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/904
在上一章我们分析了SpingBoot启动流程中实例化SpingApplication的过程。returnnewSpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);这篇文章咱么说下run()方法开始之后都做了那些事情。继续往下跟着源码进入到run()这个是比较核心的一个方法了 publicConfigurableApplicationContextrun(Stri
赛兔:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/2375
兰亭集势:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/820
woot:https://www.ikjzd.com/w/604
亚马逊居西班牙电商流量排行榜首/阿里巴巴正式在港交所上市:https://www.ikjzd.com/home/111532
口述:我长太帅老婆总怀疑我出轨丈夫妻子出轨:http://lady.shaoqun.com/m/a/33726.html
亚马逊卖家注意,这样的关键词千万别删!:https://www.ikjzd.com/home/133469

No comments:
Post a Comment